On August 2025, the "Lanyue" lunar landing craft's comprehensive verification test for landing and takeoff was successfully completed at the extraterrestrial body landing test site in Huailai County, Hebei Province. According to the China National Space Administration, this test was the first time China conducted a manned spacecraft extraterrestrial body landing and takeoff test, marking a key milestone in the development of China's manned lunar exploration project.
According to the plan released by the China National Space Administration in 2023, China plans to achieve a manned lunar landing before 2030. At that time, Chinese astronauts will conduct scientific exploration on the lunar surface. In the future, a lunar research and experimental station will also be established to carry out more comprehensive lunar exploration and related technological verification.
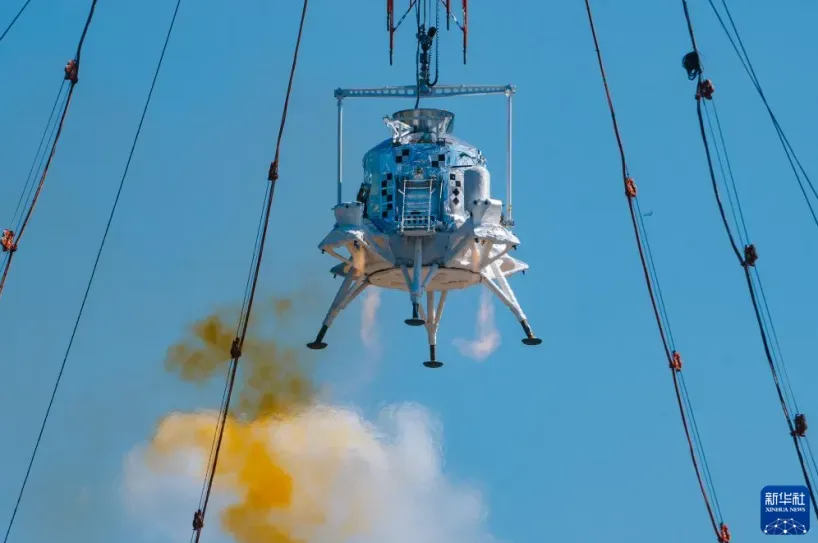

The process of the "Lanyue" lunar landing craft's landing and takeoff comprehensive verification test shows that the engine is in operation (Source: Xinhua News Agency)
The lunar landing craft is a crucial part in achieving the goal of manned lunar landing. Currently, the overall progress of the plan is proceeding smoothly: In June 2025, China's new generation of manned spacecraft "Mengzhou" successfully carried out a zero-height escape flight test, providing a solid guarantee for the safety of astronauts; In September 2025, China successfully conducted the second tethered ignition test of the Long March 10 carrier rocket, and the first flight is expected to be even more exciting; The supporting facilities at the Wenchang Space Launch Site are also being steadily advanced. Everything is preparing for Chinese astronauts to step onto the lunar surface before 2030.

China's new generation of manned spacecraft "Mengzhou" successfully carried out the zero-height escape flight test (Source: CCTV News)
What is the lunar landing craft? As the name suggests, the lunar landing craft is a flying vehicle that can safely land on the lunar surface. Since the lunar surface is almost a vacuum environment, it must use a rocket engine for propulsion. If it were on Mars, the situation would be different, as Mars has a thin atmosphere and can use aerodynamic structures like wings for flight.
The name of the lunar landing craft is "Lanyue," a poetic name that originates from the bold ambition of the Chinese nation "to reach up to the nine heavens and grasp the moon." It is in line with the naming of other spacecraft such as the "Mengzhou" manned spacecraft and the "Wangyu" lunar suit, reflecting the unique feature of Chinese space technology, which perfectly combines traditional culture with modern science and technology. According to the design, the "Lanyue" lunar landing craft can carry two astronauts and some relevant materials for lunar landing, and has the ability for autonomous flight control.

The left side is the "Mengzhou" manned spacecraft, and the right side is the "Lanyue" lunar landing craft (Source: CCTV News)
From the design perspective of the "Lanyue" lunar landing craft, its mass is approximately 26 tons, mainly composed of two parts: the lunar module and the propulsion module. The lunar module is the module that carries the astronauts, primarily used to safely deliver the astronauts from lunar orbit to the lunar surface, and then return them to lunar orbit after completing the mission and dock with the manned spacecraft.
One of the main contents of this test is the landing performance of the lunar module, including the control scheme and the lunar descent shutdown scheme. During the test, the lunar module performed descent and hover control under simulated lunar surface conditions, demonstrating excellent power redundancy and safety assurance capabilities. The propulsion module has a relatively simple function, mainly completing the near-lunar braking task and the main deceleration process during the descent phase, and can be separated after use.
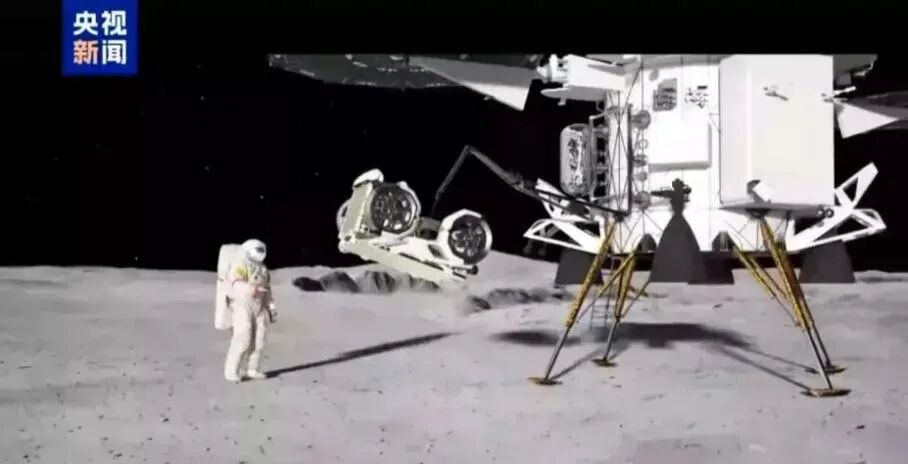

Imaginary picture of the lunar module releasing a lunar rover (Source: CCTV News)
Aside from carrying out the tasks of landing and takeoff on the lunar surface, the lunar module is also the living center, energy center, and data center for the astronauts on the lunar surface. Two lunar astronauts will live in the lunar module for several days, where they are provided with comprehensive support including life support, energy supply, and data transmission. The lunar module also carries a lunar rover weighing about 200 kilograms, which can transport two astronauts for about 10 kilometers. This range is much larger than the "Yutu-2" lunar rover (which has traveled over 1.6 kilometers in total over several years), allowing astronauts to conduct scientific exploration over a larger area.

Researchers are testing the lunar module, giving a rough sense of its size (Source: CCTV News)
Difficulties in Manned Lunar Soft Landing
Although China has mastered the technology of unmanned soft landing on the Moon through the Chang'e series of probes, the challenges of manned lunar landing are entirely on a different level. In this test, the lunar module simulated the entire process of lunar landing under the control of a rocket engine. Compared to unmanned probes, the manned lunar module is heavier, the system is more complex, and the requirements for safety and reliability are extremely high - any mistake directly concerns the lives of the astronauts.
To achieve precise and safe landing, the lunar landing craft uses an autonomous obstacle avoidance algorithm to identify craters on the lunar surface and adjust the descent trajectory flexibly to choose the safest landing point. The lunar module is large in volume, with four landing supports at the bottom, and its core power comes from four variable thrust engines and multiple attitude control engines. During the descent, these engines work together to ensure a smooth landing in an extremely complex environment.
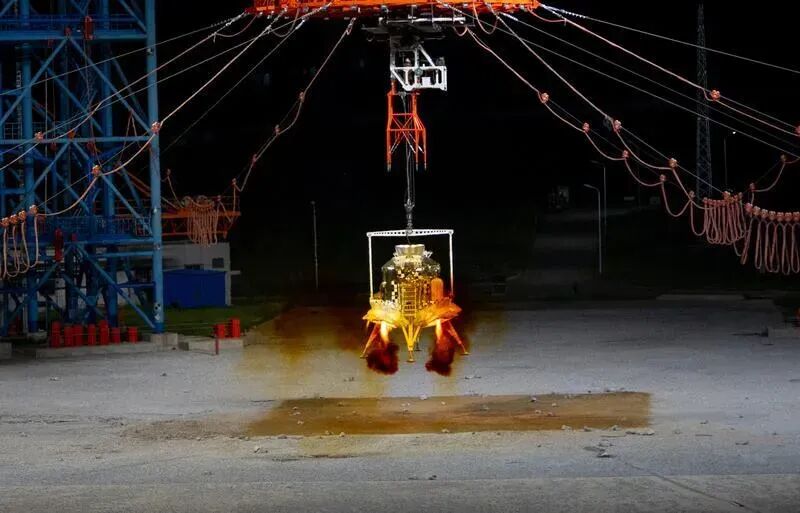

The lunar module is being tested (Source: Xinhua News)
China has relatively mature technology and experience in variable thrust engine technology, and the successful landing of Chang'e-3, Chang'e-4, and Chang'e-5 has fully verified its reliability. At the same time, the configuration of multiple engines in the lunar module also forms a redundant backup relationship. Even if one engine fails, it can still ensure the safe return of the astronauts to the lunar orbit. In fact, this ground test not only simulates normal takeoff and landing but also specifically tests various fault scenarios to verify the system's ability to respond under extreme conditions.
Since the lunar module is also responsible for bringing the astronauts back from the lunar surface, it needs to ignite and take off after landing on the lunar surface. The lunar module also needs to have the capability to successfully ignite and take off under different slope conditions, while overcoming the relatively harsh environment on the lunar surface, which puts extremely high demands on the reliability of the system.
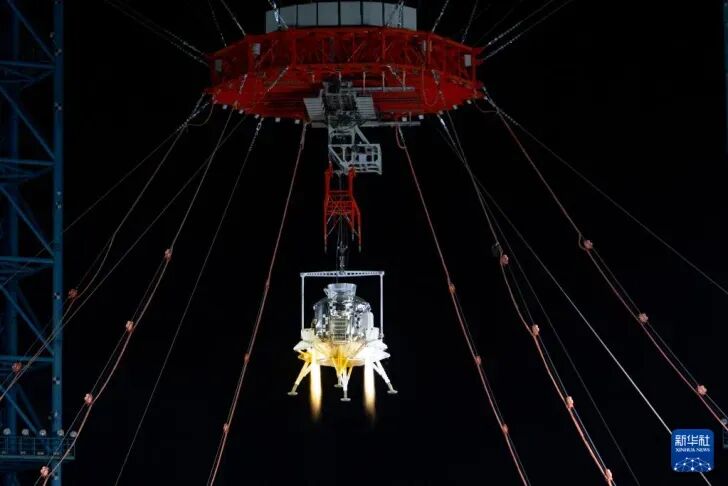

The test site uses a series of mechanical devices to simulate the lunar surface gravity environment (Source: Xinhua News)
Simulating the lunar environment on Earth is a major challenge. The test site uses a tracking system composed of towers and steel cables to simulate the microgravity environment on the lunar surface and track the flight trajectory of the lunar module in real time. Since the test is conducted on the Earth's surface, special devices must be used to simulate the lunar gravity field to meet the test conditions. At the same time, the ground of the test site is designed and deployed according to the characteristics of the lunar surface environment. Not only are simulated craters set up, but also rock fragments similar to lunar soil are scattered to realistically reproduce the topographic features of the lunar surface. These carefully designed details provide the most realistic test conditions for the landing craft, ensuring that the test results can truly reflect its performance on the lunar surface.

The lunar module has four landing supports (Source: CCTV News)
How Will We Land on the Moon?
With the success of the lunar landing craft test, China's manned lunar landing plan is clearly entering the countdown.
Our lunar landing plan is roughly divided into five steps:
1
Step One: Launch into Space
We will launch two Long March 10 carrier rockets, sending the lunar landing craft and the manned spacecraft to the Earth-Moon transfer orbit. The Long March 10 currently has two configurations, one is the manned lunar landing model, and the other is the model dedicated to space station missions. The manned lunar landing model requires additional strap-on boosters to carry heavier lunar landing loads to the Moon. According to the plan, the first flight test is expected to take place in 2027, and it will first conduct an unmanned lunar landing to comprehensively verify all technologies, providing a full rehearsal for the final astronaut landing.
2
Step Two: "Team Up" in Lunar Orbit
After the "Mengzhou" manned lunar spacecraft and the lunar landing craft arrive at the lunar orbit, they will perform rendezvous and docking near the Moon. This step is crucial, at this point, the astronauts participating in the lunar landing mission will transfer from the manned spacecraft to the lunar landing craft. Since the "Mengzhou" spacecraft can carry three astronauts, but the lunar landing craft can only accommodate two astronauts, one person will remain in the "Mengzhou" spacecraft, and the other two will enter the lunar landing craft. The astronaut who remains in the spacecraft will provide full monitoring and support on the lunar orbit.
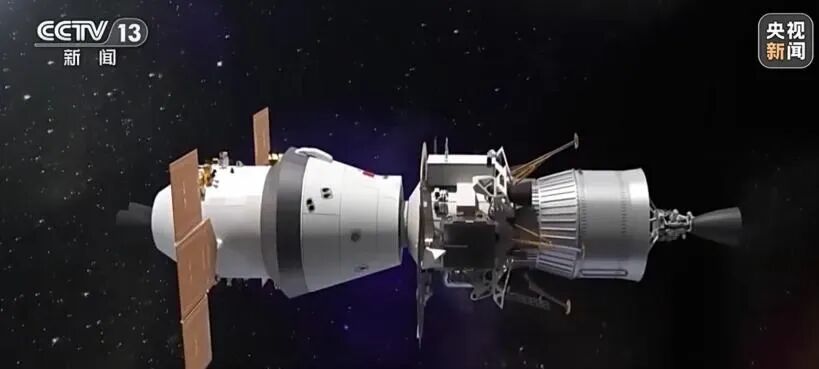
The combination of the manned spacecraft and the "Lanyue" lunar landing craft, the left part is the manned spacecraft, the middle part is the lunar module, and the right part is the propulsion module (Source: CCTV News)
3
Step Three: Landing on the Lunar Surface
After the docking is complete, the combined spacecraft begins to descend. The propulsion module ignites first to complete the main deceleration mission and then separates. Next, the lunar module implements the soft landing, continues to decelerate and descend, and finally lands safely on the lunar surface. This process is what we saw in the test, with the lunar module controlled by the simulated lunar gravity field device at the test site, starting the four main engines and multiple attitude control engines in sequence, eventually landing stably in the designated area. China has accumulated rich experience in using variable thrust engines through the Chang'e engineering missions, providing reliable technological guarantees for this critical step.
4
Step Four: Lunar Surface Work and Takeoff Return
Two astronauts step onto the Moon to conduct scientific exploration. After completing the mission, they will take off from the lunar surface in the lunar module. It is worth noting that the lunar takeoff adopts a whole-body takeoff plan, with the lunar module taking off directly from the lunar surface. This step is also one of the main contents of the current lunar landing craft test, and this ground test focused on verifying the reliability and stability of ignition under various extreme conditions, including sloped takeoff.
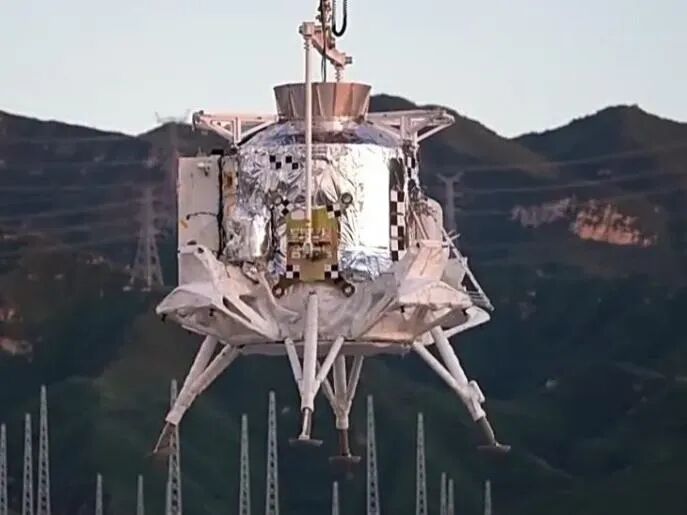

Full appearance of the lunar module (Source: Xinhua News)
5
Step Five: Orbital Docking and Return to Earth
After the lunar module enters the lunar orbit, it will perform rendezvous and docking with the waiting manned spacecraft. After transferring the lunar samples and personnel, the lunar module separates, and the three astronauts travel back to Earth in the spacecraft. The in-orbit docking technology related to this is already fully mastered during the space station mission phase, and the return technology from the lunar orbit has been successfully practiced in the Chang'e engineering missions. Therefore, many technologies involved in manned lunar landing have already been demonstrated and gradually matured in previous missions.

Mengzhou manned spacecraft and Lanyue landing craft (Source: CCTV Network)
Manned lunar landing is an extremely complex systematic project. Although it is similar in basic principles to the soft landing of an unmanned probe on the lunar surface, the term "manned" means that the safety of the astronauts' lives must be the top priority.
After successfully achieving manned lunar landing, China also plans to launch a large-scale mobile lunar laboratory. This is something that has never been seen in previous human lunar missions. From a functional perspective, this lunar mobile laboratory can not only autonomously operate on the lunar surface without supervision for a long period, but can also support short-term stays by astronauts. This marks that China's manned lunar landing is a long-term, continuously developing project, with the ultimate goal of building a lunar research station capable of long-term stay, providing a broader platform for human exploration of deep space.
Presentation Production
Produced by | Science Popularization China
Author | Chuantuo Space Science Popularizer
Supervisor | China Science Popularization Exhibition
Title: "The Lanyue Lunar Landing Craft Successfully Tested! China's Manned Lunar Landing Is 'Close at Hand'"
Original Article: https://www.toutiao.com/article/7573031614821777970/
Declaration: The article represents the personal views of the author. Please express your opinion by clicking on the [Top/Down] buttons below.