
Moore Threads, known as "NVIDIA of China," officially launched its application for the Sci-Tech Innovation Board (STAR Market) on November 24. The issue price is 114.28 yuan per share, setting a new record for the highest IPO price in A-shares in 2025. The company raised approximately 8 billion yuan, far exceeding the average scale of 803 million yuan for the STAR Market in the first half of the year.
Given the general caution in the capital market, why has Moore Threads received such a high valuation?
Single-card computing performance approaches NVIDIA RTX 3060
On November 21, during an online investor exchange meeting held by Moore Threads for its STAR Market listing, the company's founder Zhang Jianzhong discussed the gap with giants like NVIDIA and AMD.
Compared to international leaders like NVIDIA and AMD, the company still needs to continuously improve in terms of technical accumulation and product performance. However, the company's products have already reached or approached international advanced levels in some performance indicators, achieving replacement for some "bottleneck" products. For example, the FP32 computing performance of the MTT S80 graphics card is close to that of NVIDIA RTX 3060.

Single-precision floating-point computing power is a core indicator for measuring GPU computing capabilities, directly affecting the speed and efficiency of high-parallel tasks such as graphic rendering, deep learning training, and general scientific computing.
The MTT S80 has single-precision floating-point computing power comparable to mainstream graphics cards from a few years ago, indicating that domestic GPUs now have the computing power to meet the needs of most games, graphics, and small-to-medium-scale AI tasks. This marks a substantial breakthrough in key "bottleneck" technologies in China, and in the long run, it makes future GPU price reductions and stable supply possible.
As the only company in China that has achieved full-function GPU mass production, Moore Threads is considered the most similar Chinese company to NVIDIA.
Founder Zhang Jianzhong served as Vice President of NVIDIA and General Manager of China for 14 years, and led the establishment of NVIDIA's complete ecosystem in China.
In addition, several core executives come from NVIDIA: Zhou Yuan, former Senior Director of Marketing Ecosystem at NVIDIA, Zhang Yubo, former GPU Architect at NVIDIA, and Yang Shangshan, former Deputy General Manager and 8-year GPU Architect at NVIDIA, all hold key positions in the company.
Therefore, the market often refers to it as a "NVIDIA student" in China, and even when it was just founded, it was seen as a GPU unicorn based on its team background.
In terms of technology, Moore Threads adopts a full-function GPU design, covering four engines: AI computing, graphic rendering, video encoding and decoding, and scientific computing. It is highly compatible with NVIDIA's CUDA ecosystem, and the released MUSA architecture aims to achieve "one-click migration."
The currently released "Sudi", "Chunxiao", "Quyuan" series chips have 7nm process, large-scale computing cluster capabilities, and can directly compete with NVIDIA products in high-performance computing and large model training scenarios.

In product layout, Moore Threads also precisely replicates NVIDIA's product matrix. From the beginning, it has simultaneously focused on B-end AI data centers (Kua'e Thousand Card Intelligent Computing Cluster) and C-end gaming graphics cards (such as MTT S80).
By the end of 2024, Moore Threads had 425 authorized patents, covering key technologies such as chip architecture, AI acceleration, and driver software, and had built up over a thousand ecological partners, forming a complete industry chain from chips to software.
High R&D investment leads to consecutive losses
Although Moore Threads shows cutting-edge innovation and potential in technology and business, as a young company that has only been established for five years, it still faces challenges in technological gaps, financial losses, and ecological barriers, especially the high R&D costs, which are the core reason for the company's continued losses.
From 2022 to the first half of 2025, Moore Threads' R&D investments were 1.116 billion yuan, 1.334 billion yuan, 1.359 billion yuan, and 557 million yuan, totaling approximately 4.366 billion yuan.
The R&D intensity that can be described as "burning money" is behind the extremely high technical barriers in the GPU industry. Each link, from hardware design to software ecosystem, requires long-term investment, which is an unavoidable problem.
On the other hand, high R&D costs have also brought back market share.
From 2022 to 2024, Moore Threads' revenue increased year by year, reaching 46.088 million yuan, 124 million yuan, and 438 million yuan respectively, with a compound growth rate of 208.44%; non-GAAP net losses were 1.412 billion yuan, 1.69 billion yuan, and 1.5 billion yuan respectively.
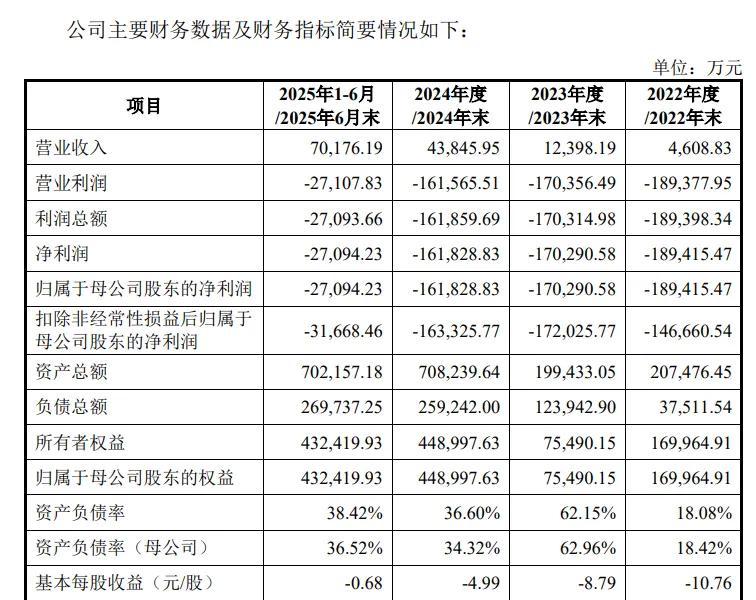
In the first half of 2025, Moore Threads' revenue was 702 million yuan, exceeding the total revenue of the past three years, but it was still in a loss state. The同期 attributable net profit was -271 million yuan. As of June 30, 2025, the company's cumulative unremedied loss was approximately 1.48 billion yuan.
In the prospectus, Moore Threads also made predictions about future development: With continuous breakthroughs in AI applications such as large models, embodied intelligence, and intelligent driving, the demand for computing power in the domestic market continues to rise, and the domestic GPU market size will continue to grow. It is expected that the company could achieve profitability as early as 2027.
Although the prospects are optimistic, Moore Threads is still in a squeezed position both inside and outside the industry.
On the industry level, NVIDIA and AMD, with their years of first-mover advantage, technical accumulation, and ecological barriers, have formed strong market shares, particularly dominating the high-end smart computing field; on the domestic level, the追赶 of domestic GPU companies such as Bitmain Technology and Muxi Integrated Circuits has also intensified competition, potentially further compressing the company's profit margins.
On the technical level, as mentioned earlier, the RTX 3060 was released in 2021, while the MTT S80 was launched in 2023, meaning that the product performance is still two generations behind the forefront.
Although the MUSA architecture launched by Moore Threads has achieved a technological breakthrough, the prospectus shows that the company still has significant shortcomings in core technology accumulation, supply chain self-reliance, and product performance, and these gaps exist objectively in the short term, especially in the software ecosystem and application scenario adaptation, which significantly affects the speed of market expansion.
For Moore Threads, this is undoubtedly a tough battle. In addition to the short-term confidence brought by the IPO funds, the greater challenge lies in how to win a place in the fiercely competitive GPU market through continuous technological iteration and investment.
Original article: https://www.toutiao.com/article/7576479806804460059/
Statement: The article represents the views of the author. Please express your attitude by clicking on the [Up/Down] buttons below.